- Joined
- Dec 4, 2011
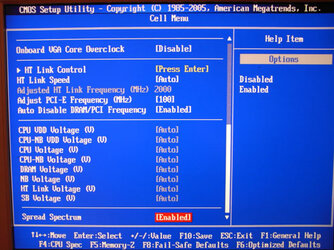
Can someone with stronger understanding of matter explain each Voltage settings, because many users (including me) found it very confusive to handle with so many similar settings? My primary goal here is achieving stable undervolted CPU configuration, but I was unable to distinguish between following:
CPU VDD Voltage
CPU-NB VDD Voltage
CPU Voltage
CPU NB Voltage
DRAM Voltage
NB Voltage
HT Link Voltage
SB Voltage

CPU VDD Voltage
CPU-NB VDD Voltage
CPU Voltage
CPU NB Voltage
DRAM Voltage
NB Voltage
HT Link Voltage
SB Voltage